Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsumoto, Ayumu; Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
Miyabe, Masabumi; Jung, K.; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
Remote isotopic analysis for highly radioactive fuel debris containing various actinides, fission products and the other reactor materials is expected to be needed for the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan. This is because the information on the amount of fissile materials in the debris is of great importance for the purpose of safeguard verification and prevention of re-criticality accident. However, to decrease radiation dose to the analytical workers handling the debris, traditional analytical techniques such as radiometric and radiochemical methods are inadequate and an alternative technique is needed. For this reason, we are developing remote spectroscopic techniques (LIBS and LAAS) for debris analysis using laser ablation process. Laser ablation absorption spectroscopy (LAAS) is the technique by combining resonance absorption spectroscopy and laser ablation. In this technique for nuclear fuel materials, one uses the probe laser whose frequency is tuned to the resonance line of the specific isotope of U or Pu and determines the isotopic abundance from the measured absorbance. For realization of highly sensitive and isotope-selective analysis, it is necessary to optimize experimental conditions to decrease kinetic energy of the ablated species and the number of ionic species so as to reduce Doppler and Stark effects. For this optimization, we have studied the temporal and spatial variations in the density distribution under various background gas conditions. Using the optimum conditions, we have measured isotope-selective absorption spectra of U and Pu and evaluated several analytical performances of LAAS.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
For quantitative analysis using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy, many efforts for identification and analysis of the spectrum are required. The nuclear-fuel debris from the accident at the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi NPS is mainly composed of nuclear fuel (uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu)), actinides, fission products, and cladding tubes (zirconium (Zr)). Concrete (calcium), stainless steel (iron, nickel, and chrome) in the structural materials, and the like may also be included in debris. We analyzed the LIBS spectrum using "spectrum analysis using the least-squares method" as technique not to need high specialty identification of the complicated spectrum analysis.
Nishimura, Akihiko; Yamada, Tomonori; Shibata, Takuya; Furusawa, Akinori; Takenaka, Yusuke*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Saeki, Morihisa*; Yomogida, Takumi; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Takumi*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Oba, Hironori*
no journal, ,
The structures of isoploymolybdate(VI) were investigated by using laser Raman spectroscopy. The assignment of the Raman spectra showed presence of the [Mo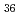 O
O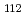 (H
(H O)
O) ]
]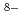 in the 0.2 M HNO
in the 0.2 M HNO and the [Mo
and the [Mo O
O (H
(H O)]
O)] in the 1.0 M HNO
in the 1.0 M HNO . To extract the spectrum of the intermediate species, we applied chemometrics analysis to a series of the observed spectra. The analysis revealed presence of one intermediate [Mo(VI)
. To extract the spectrum of the intermediate species, we applied chemometrics analysis to a series of the observed spectra. The analysis revealed presence of one intermediate [Mo(VI) O
O ]
]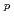 species in the 0.5 M HNO
species in the 0.5 M HNO . The intermediate species were assigned to [Mo
. The intermediate species were assigned to [Mo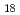 O
O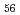 (H
(H O)
O) ]
]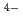 with the aid of X-ray absorption spectroscopy.
with the aid of X-ray absorption spectroscopy.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Matsumoto, Ayumu; Miyabe, Masabumi; Ikeda, Yuji*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Taira, Takunori*
no journal, ,
For the decommissioning of "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (F1NPS)", widely basic R&D and matting for actual application for decommissioning technology will be strongly required. CLADS/JAEA is one of the key institute for strategic promotion of Decommissioning Science on F1NPS. As for the development of rapid, easy, onsite and in-situ remote diagnostic/analysis techniques under extremely high radioactive condition, the concept of probing by light and diagnostic by light with radiation resistant optical fiber will be one of the simple, powerful and applicable choices as the innovative development based on laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) technology. Optical fiber based LIBS is developed for in-core and in-situ elemental analysis of debris and its activity is performed under severe environmental conditions such as high radiation field of about 10kGy/h and under water. Long pulse laser, microwave assisted LIBS and microchip laser are also introduced for more high sensitivity.